A Visual Love Letter to the Queen City Memory Café
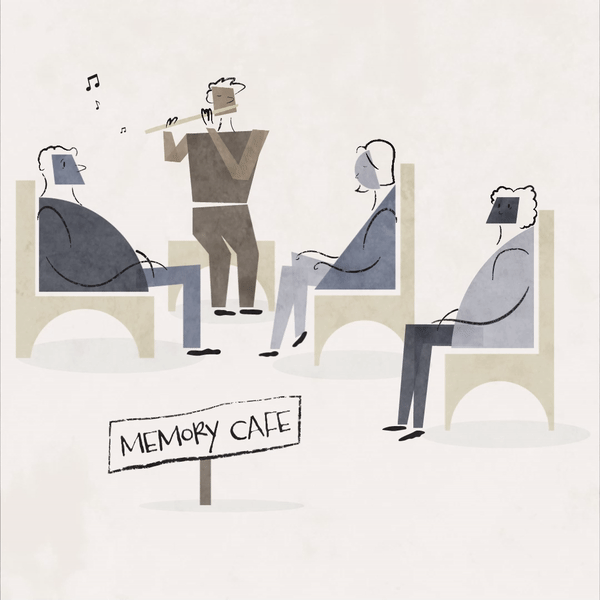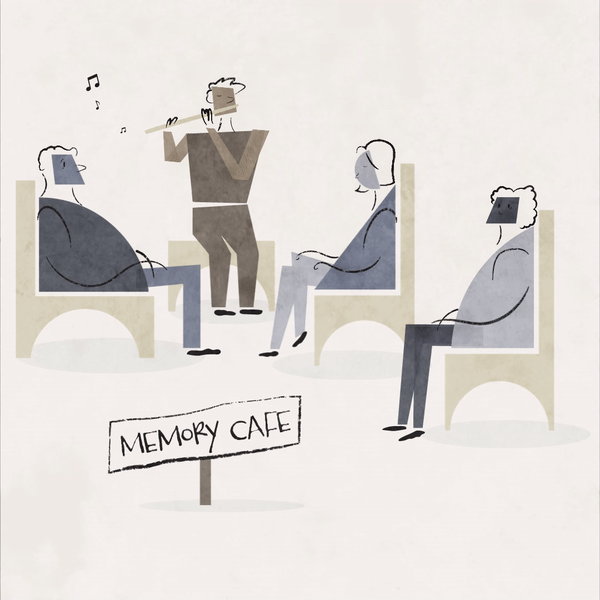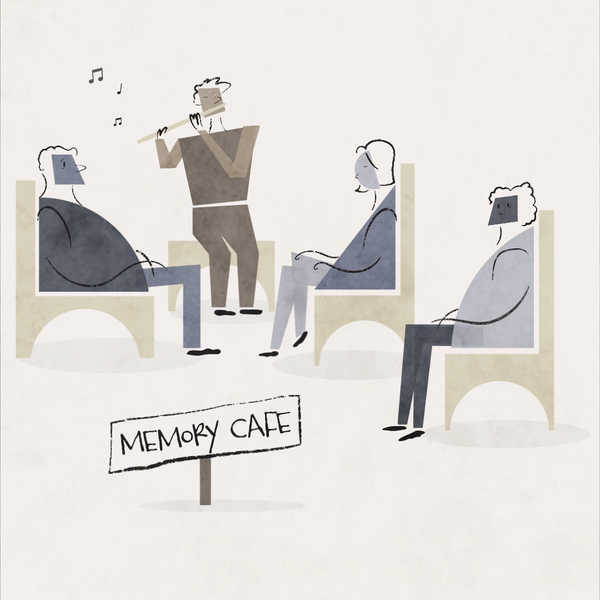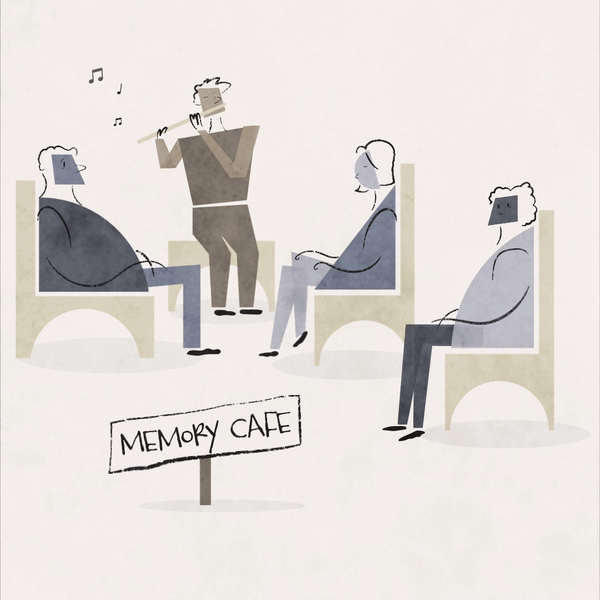
The Memory Café
A Memory Café is a monthly event that offers an inclusive space for people living with dementia and their loved ones to laugh, learn, and connect with people who understand. Memory Cafés are found all over the world, each striving to provide support for participant’s social needs by lessening feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Humor
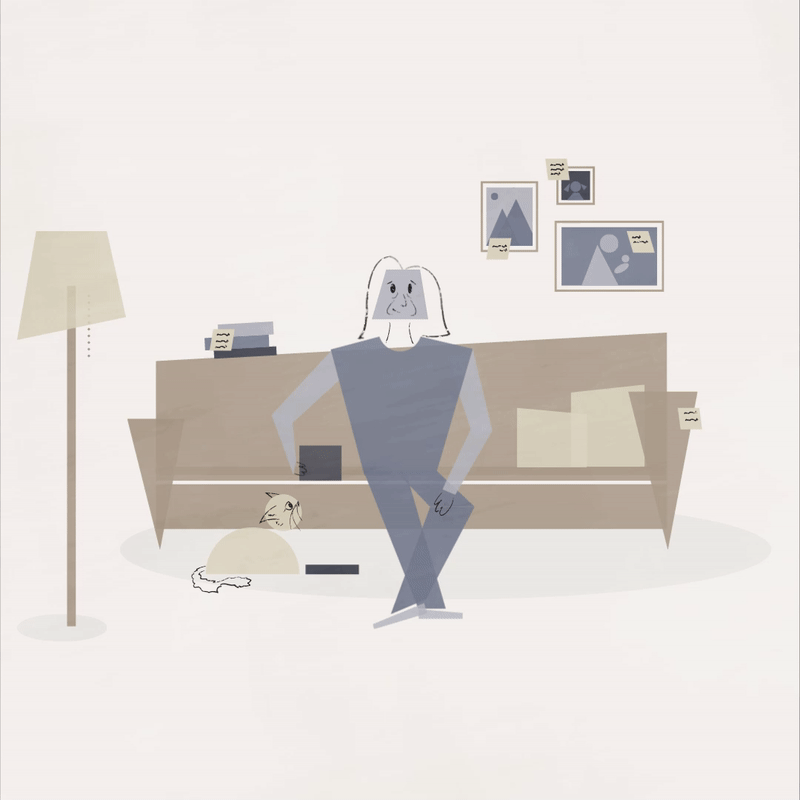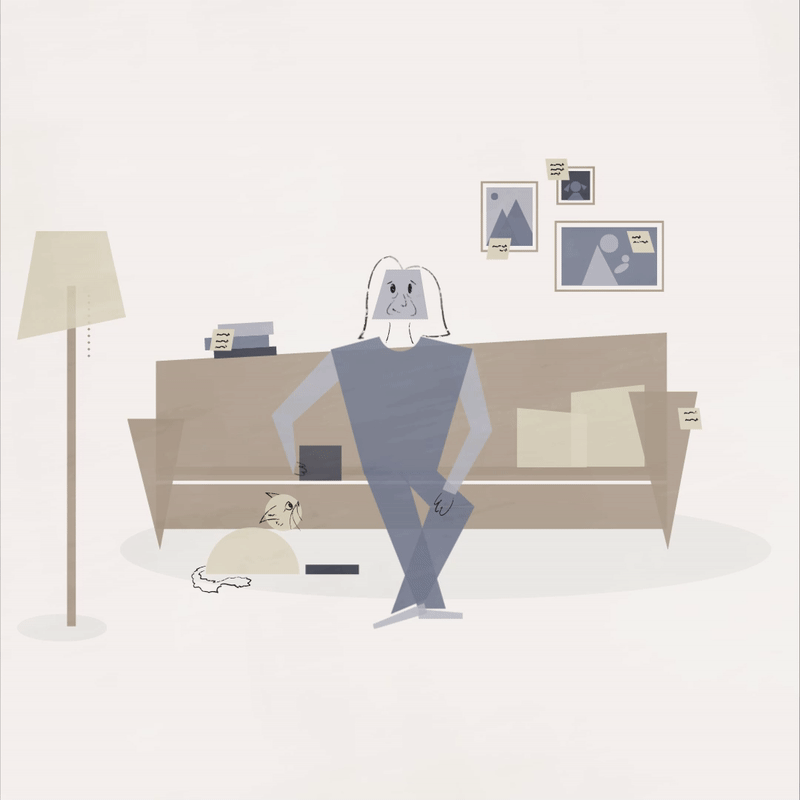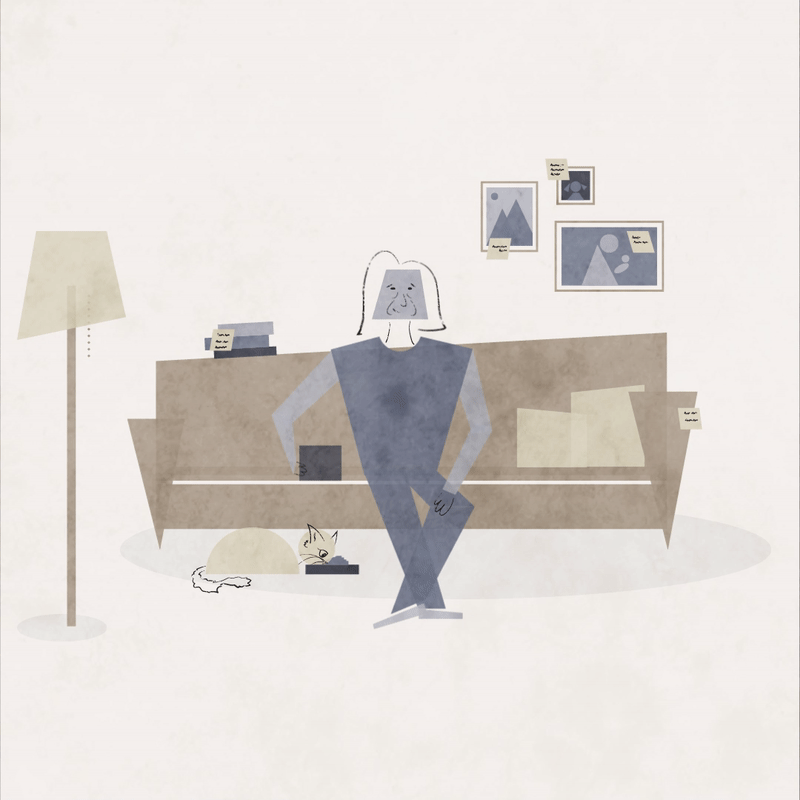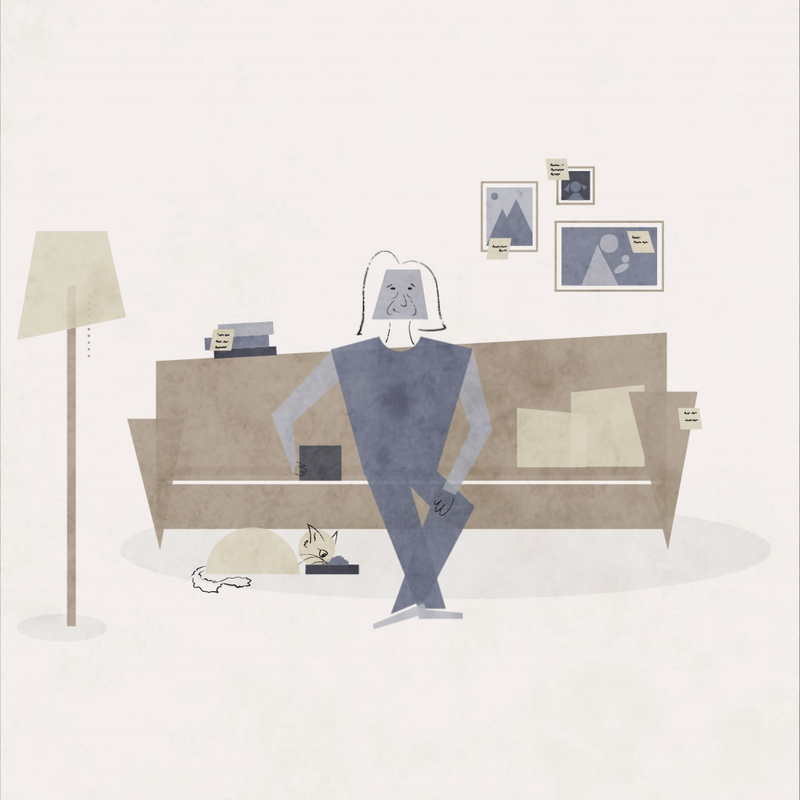
Dementia is a very serious disease, but sometimes it’s okay to look at the lighter side of one’s circumstances and laugh. Humor can relieve stress, provide mental stimulation and strengthen relationships. This animation of a woman who repeatedly feeds her cat serves as an invitation to smile.
Grief
For many of us, four years can mean self-growth, new beginnings, and reimagining ourselves. However, for someone living with dementia, four years can be characterized by a sense of loss, grief and fear.
Neuroscience
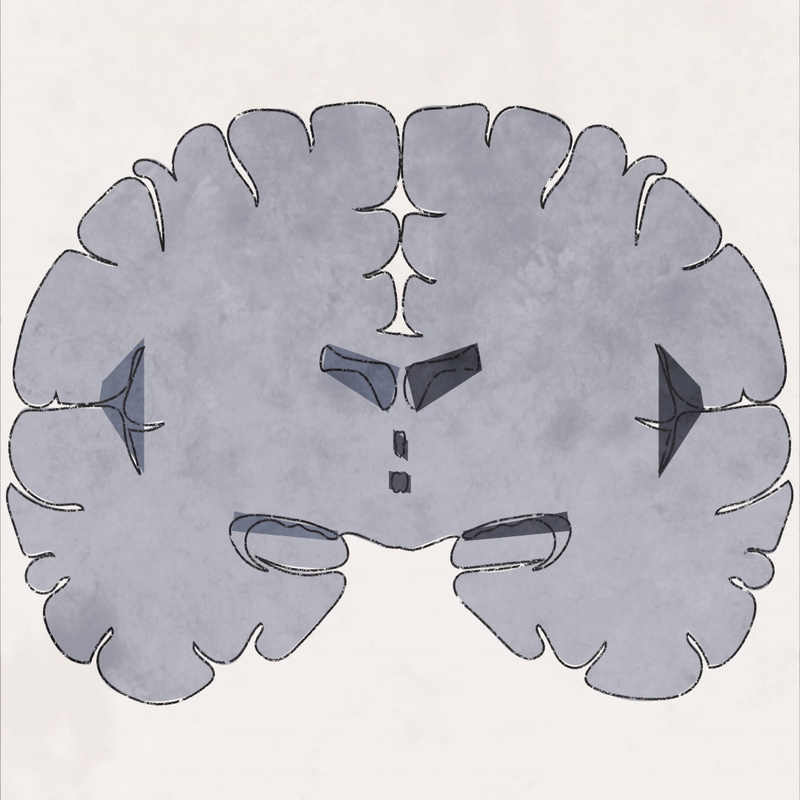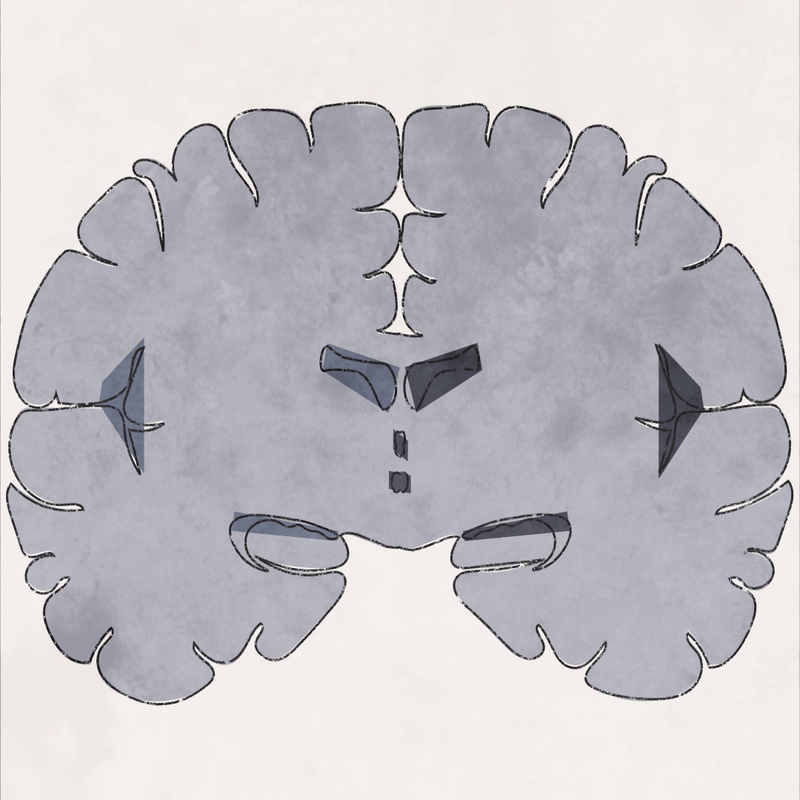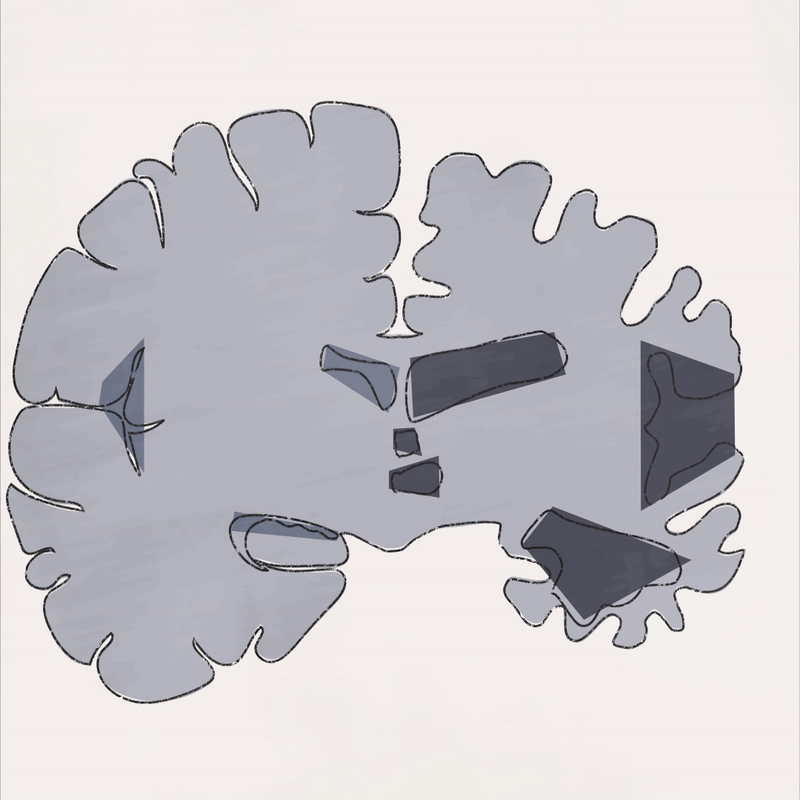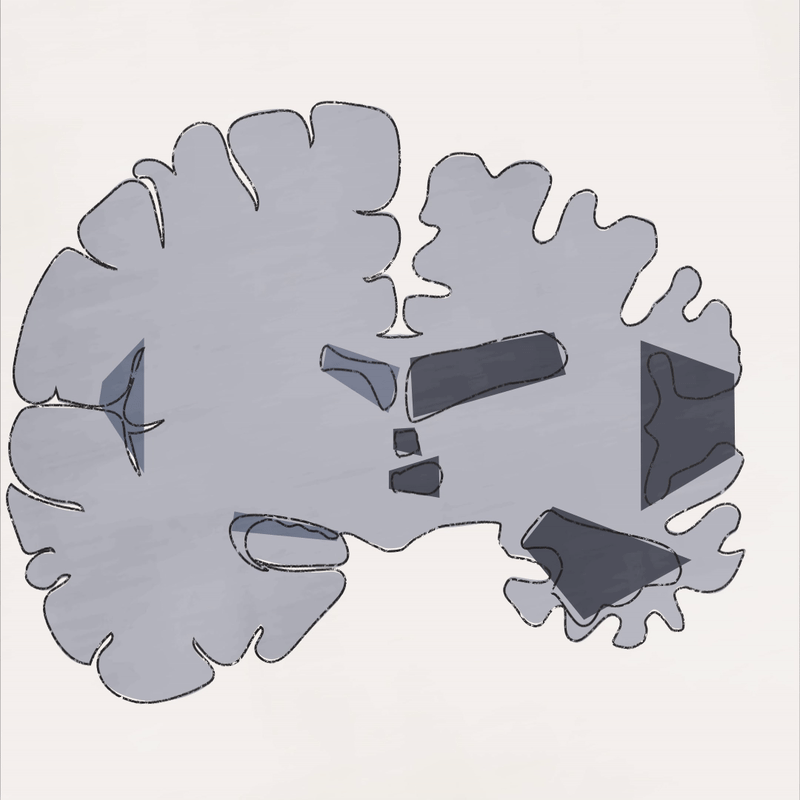
Dementia is caused by damage to brain cells which interferes with their ability to communicate with each other.
Part 1: Brain atrophy - the loss of brain cells called neurons - is widespread in the later stages of Alzheimer’s disease.
Part 2: In a brain with Alzheimer’s, abnormal levels of beta amyloid plaque clump together and collect between neurons. There are also abnormal accumulations of a protein called tau that collect inside neurons to form neurofibrillary tangles.
Part 3: There is some evidence that inflammatory processes in the brain result in increased damage to the myelin sheath.